
Abstract
This study will demonstrate the use of the ATCC Vibrio campbellii Panel (ATCC MP-6) as a nonpathogenic model for AI-2-based quorum sensing pathways.
Download a PDF of this application note
Download NowIntroduction
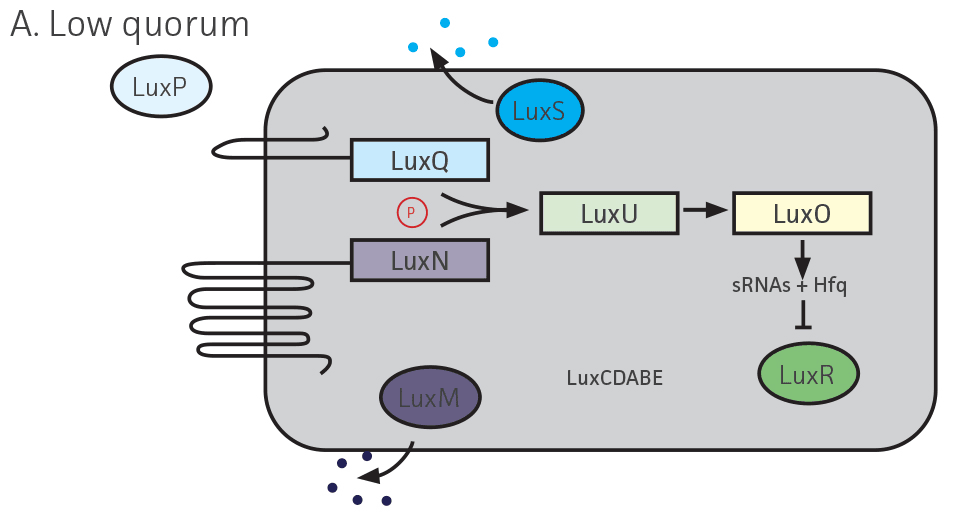
In many prokaryotes, cooperative behaviors are regulated through a density-dependent, signal-mediated communication system termed quorum sensing (QS)1 When a bacterial population reaches a critical threshold, autoinducer signaling molecules (AI) specifically bind to a cognate regulatory protein or activate a 2-component signal transduction system, leading to the regulation of group behaviors. In the marine organism Vibrio campbellii, AI signals (AI-1 and AI-2) and cognate regulators are used to regulate bioluminescence1 (Figure 1). Since its discovery, AI-2 has proven ubiquitous within interspecies and intraspecies communication, including that of pathogenic microorganisms.2 Here, we show a panel of 9 V. campbellii strains displaying wild-type or varying mutational phenotypes for use as a nonpathogenic model in the analysis of AI-2-based QS systems.
Materials and methods
Nine V. campbellii strains were phenotypically analyzed for QS proficiency by monitoring the bioluminescence production of genotypically diverse strains that were plated together in pairs on Autoinducer Bioassay Medium.1,3-6
Results and discussion
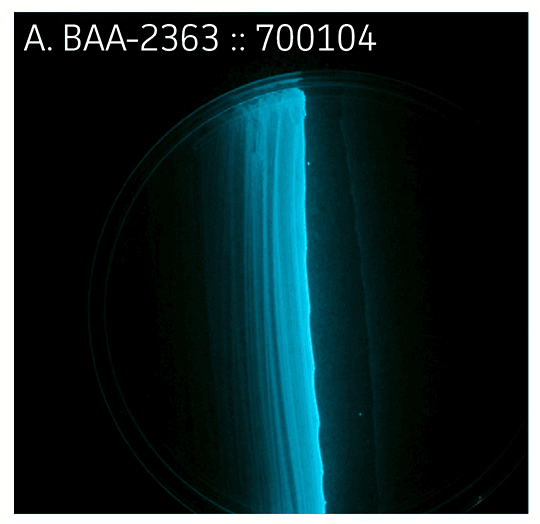
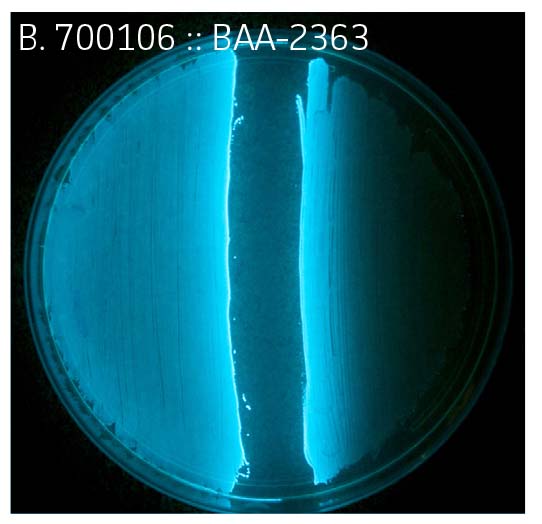
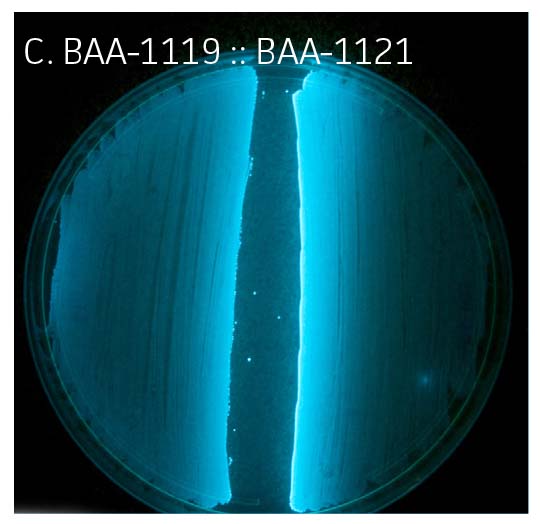
Upon analysis of paired strains, it was determined that bioluminescence could be restored in strains lacking regulator and/or AI production if the adjacent strain was proficient in that characteristic (Figure 2A-C, Table 1). Bioluminescence could not be restored in strains lacking part of the luxCDABE operon, which encodes for bioluminescence (Figure 1, Figure 2D, Table 1).
 |
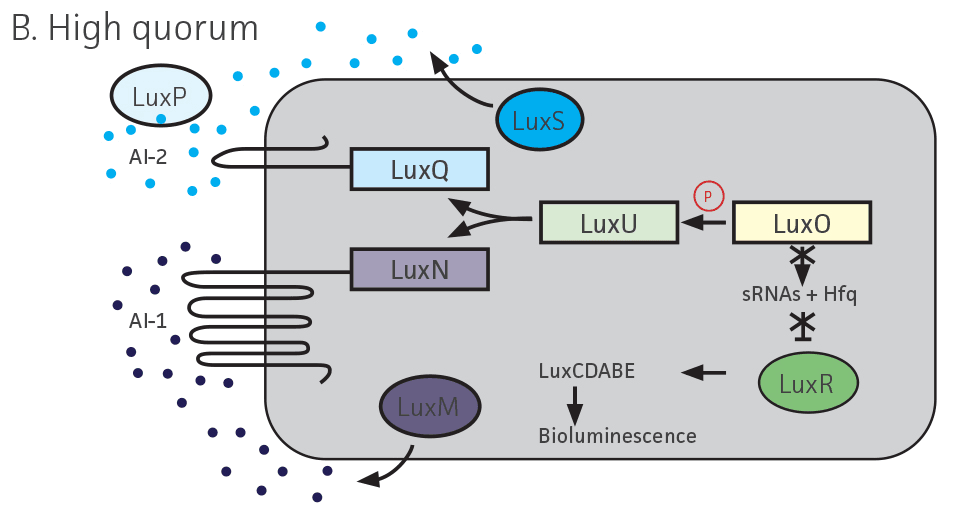 |
Figure 1. Quorum sensing
 |
 |
 |
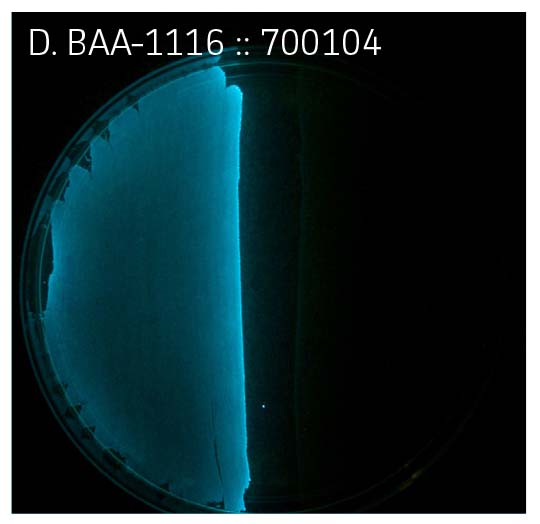 |
Figure 2. Bioluminescence
Table 1. ATCC Vibrio campbellii panel. (ATCC MP-6)
| Autoinducers | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1+, 2+ | 1+, 2+ | 1+, 2+ | 1+, 2+ | 1+, 2+ | 1-, 2+ | 1+, 2- | 1+, 2- | 1-, 2- | ||
| Sensors | ATCC number | 700104 | 700106 | BAA-1116 | BAA-1117 | BAA-1118 | BAA-1119 | BAA-1120 | BAA-1121 | BAA-2363 |
| luxA- | 700104 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1+ , 2- | 700106 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1+ , 2+ | BAA-1116 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1- , 2+ | BAA-1117 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1+ , 2- | BAA-1118 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1- , 2+ | BAA-1119 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1+ , 2+ | BAA-1120 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1- , 2+ | BAA-1121 | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - |
| 1+ , 2+ | BAA-2363 | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - |
Sensor 1 = LuxN; Sensor 2 = LuxQ; Autoinducer 1 = AI-1; Autoinducer 1 AI-2; (+) = Light observed; (-) = No light observed.
Conclusion
The characterization of these V. campbellii strains illustrates that ATCC MP-6 is well suited as a nonpathogenic model for the analysis of AI-2-based, 2-component regulatory QS pathways.
Download a PDF of this application note
Download Now
References
- Bassler B, Wright M, Silverman M. Multiple signaling systems controlling expression of luminescence in Vibrio harveyi: sequence and function of genes encoding a second sensory pathway. Mol Microbiol 13: 273-286, 1994.
- Galloway WR, et al. Quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria: small-molecule modulation of AHL and AI-2 quorum sensing pathways. Chem Rev 111: 28-67, 2011.
- Surette MG, Miller MB, Bassler BL. Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Vibrio harveyi: a new family of genes responsible for autoinducer production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96: 1639-1644, 1999.
- Waters CM, Bassler BL. The Vibrio harveyi quorum-sensing system uses shared regulatory components to discriminate between multiple autoinducers. Genes Dev 20: 2754-2767, 2006.
- Bassler BL, Greenberg EP, Stevens AM. Cross-species induction of luminescence in the quorum-sensing bacterium Vibrio harveyi. J Bacteriol 179: 4043-4045, 1997.
- Bassler BL, Wright M, Silverman MR. Sequence and function of LuxO, a negative regulator of luminescence in Vibrio harveyi. Mol Microbiol 12: 403-412, 1994.
- Lin B, et al. Comparative genomic analyses identify the Vibrio harveyi genome sequenced strains BAA-1116 and HY01 as Vibrio campbellii. Environ Microbiol Rep 2(1): 81-89, 2010.