Why it’s important
Annually, 60 to 70 million people are affected by diseases or disorders within the GI tract, making this an important therapeutic target.1 Disruption of the intestinal barrier can lead to numerous immune and inflammatory conditions ranging from acute, such as gastroenteritis, to chronic responses, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), food allergies, celiac disease, and diabetes.2 Most GI studies have been conducted on in vitro cell models to mimic cellular and molecular events in interaction with the surrounding environment. To be more physiologically relevant to the human GI system, scientists need to use diverse cell types to evaluate the cross talk between the epithelial layer, the gut microbiota, and the gut immune system.
What’s the solution?
Firstly, improvements to models of the intestinal barrier created by including immune cells in culture have been made over the past two decades as the GI tract houses 70-80% of the body’s immune cells within the lamina propria.2 Scientists can utilize known cell lines that have previously been associated with other areas, such as cancer research, but can apply such cell lines to GI research as well. Although most of the cancer cell lines may not express typical function of their original tissue, there is a group of cell lines that still maintain normal phenotype and physiological relevance. The cell lines Caco-2 (ATCC® HTB-37™), HT-29 (ATCC® HTB-38™), and LS 180 (ATCC® CL-187™) are great examples of this phenomenon. The Caco-2 cell line can differentiate into functional enterocytes; it is widely used for GI studies, including studies of intestinal transport, absorption, bioavailability, and permeability of the intestinal barrier to food and drug components. HT-29 is known to be used for studying anticancer drugs for colorectal cancer, but when treated with methotrexate, it is a mucin-secreting cell line that is ideal for simulating the mucosal conditions of the GI tract.2 LS 180, as well as its derivative LS 174T, are also mucin-secreting cell lines for research of mucin secretion and regulation, but they are more widely known for their property of producing carcinoembryonic agents in cancer research.2 THP-1 (ATCC® TIB-202™) is an immune cell line known for its use in leukemia research, but it is also one of the best models for studying monocyte and macrophage functions.2 When these cells are cocultured with intestinal epithelial cells, such as the popular Caco-2 line, the chemical interactions between these two types of cells provide insight into GI inflammation. To take the model a step closer to physiological relevancy, Caco-2, HT-29 with methotrexate (HT29-MTX), and THP-1 can be used together as a tri-culture system to mimic the intestinal barrier responses during gut inflammation.
How ATCC can help
Here at ATCC, we have a collection of well-characterized and normal functionally maintained cell lines that can be used together to achieve a physiologically relevant culture model system for GI research. Our collection includes colonocytes, enterocytes, goblet cells, intestinal neuroendocrine cells, enteroendocrine cells, and immune cells. This list will continue to grow as our team is dedicated to enhancing GI research and is continually searching for new products to fill these gaps in the community.
Did you know?
ATCC's portfolio of gastroenterology cell models includes normal, adenocarcinoma, and carcinoma cells.
Meet the authors
Karlie Wysong, MS
Senior Biologist, ATCC
Karlie Wysong is a Senior Biologist at ATCC. She obtained her bachelor’s degree in Biochemistry with a minor in Chemistry, followed by her master’s degree in Pharmaceutical Sciences. She has a background in computational biochemistry and cell and gene therapy research. At ATCC, Karlie is on the Content and Accessioning team within the Cell Biology department, responsible for the acquisition and bioproduction of new cell lines to add to ATCC’s General Collection catalog.
Paul Lovell, PhD
Associate Scientist, ATCC
Paul Lovell is an Associate Scientist that joined ATCC in 2022. He obtained his bachelor’s of science degree in biotechnology from Syracuse University in 2017 and his doctoral degree in 2022 from the University of Nebraska Medical Center in Omaha focused in Pharmaceutical Sciences. At ATCC, Dr. Lovell is working within the Cell Biology group on the Content and Accessioning team.
Explore related resources
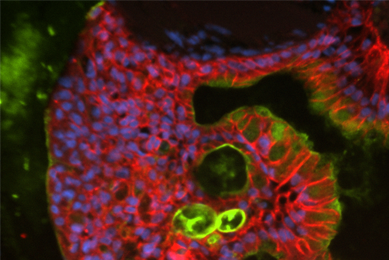 Application note
Application note
Protocol for the Thawing, Expansion, and Cryopreservation of Mouse Small Intestinal Organoids
Here, we describe a protocol for the initiation, culture, and subsequent cryopreservation of mouse small intestinal organoids starting from previously cryopreserved primary tissue–derived organoids.
More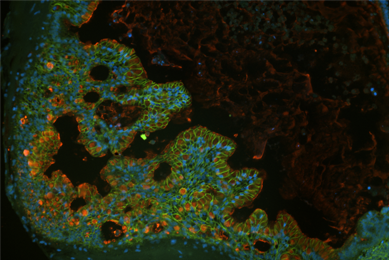 Application note
Application note
Directed Differentiation of Gastrointestinal Epithelial Organoids
Three human iPSC lines were tested for their ability to generate gastrointestinal organoids using defined culture media in a 2-D/3-D culture system using ATCC Cell Basement Membrane.
MoreDoes all Disease Begin in the Gut? Monitoring the Barrier Function of an In Vitro Gut Mimic
Here we discuss incorporating ATCC cells into studies using a novel method to measure TEER in a complex gut model.
MoreReferences
- Haddad MJ, et al. Complexification of In Vitro Models of Intestinal Barriers, A True Challenge for a More Accurate Alternative Approach. Int J Mol Sci 24(4): 3595, 2023. PubMed: 36835003
- National Commission on Digestive Diseases. Opportunities & Challenges in Digestive Diseases Research: Recommendations of the National Commission on Digestive Diseases. Bethesda, MD: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2009. Accessed June 24, 2025. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/about-niddk/strategic-plans-reports/opportunities-challenges-digestive-diseases-research-recommendations-national-commission